Configuring extended capabilities using additional tools and data sources
Extended capabilities allow agents to go beyond answering questions. The platform provides a suite of configurable tools that extend your agent's functionality, allowing it to run code, work with structured inputs, access external systems, or perform other tasks.
📝 Note: When creating a new AI agent or editing an existing one, click Tools to view and link available tools to your agent.
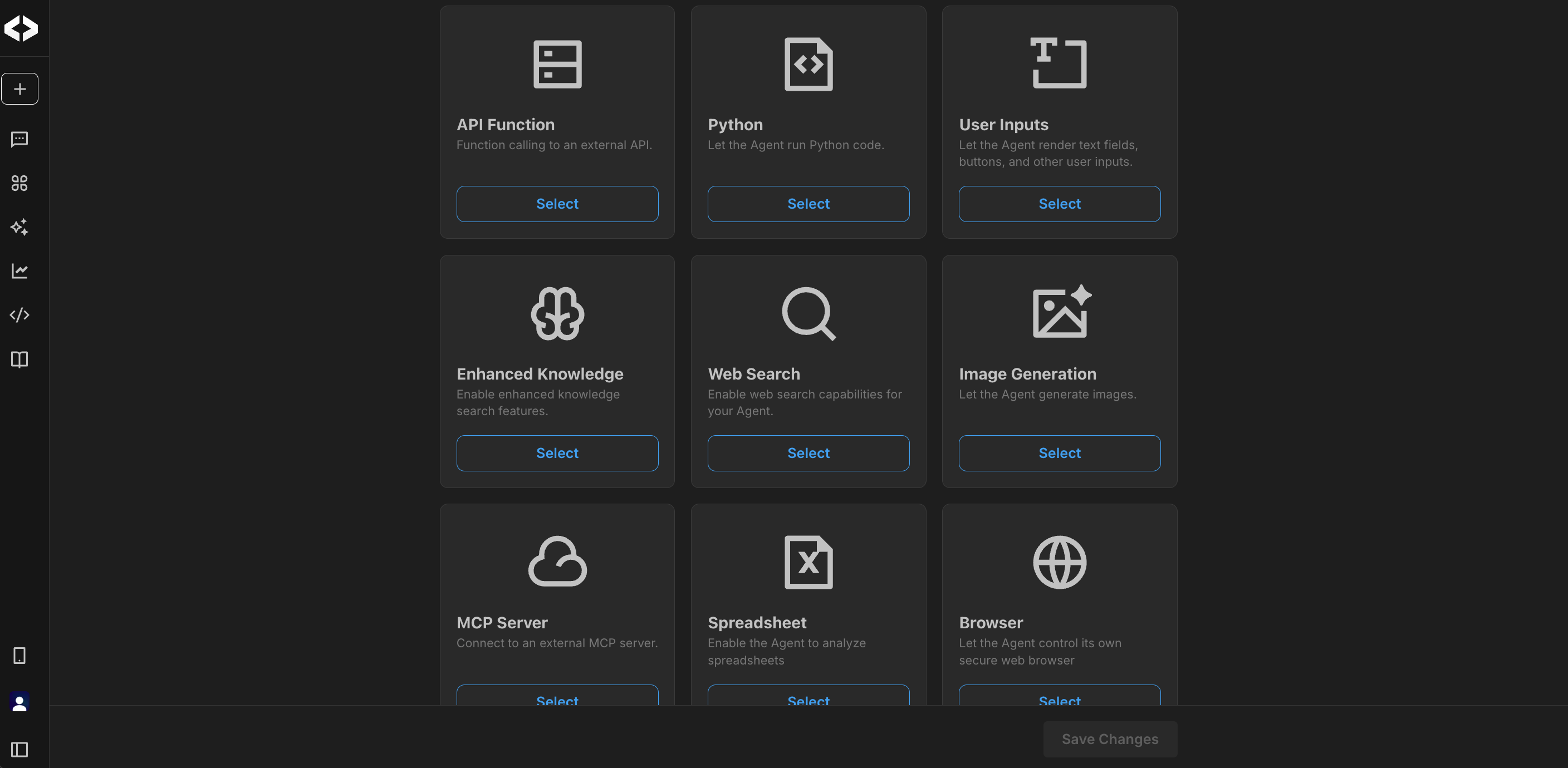
API Function
Add API actions so that an agent can call an external API. This is useful when the agent needs to read from or write to other systems, such as internal services or third-party platforms. For more information on how to configure APIs, see Add API Actions.
Python
Enabling Python allows your agent to perform actions on files and execute custom Python scripts generated in response to specific queries. This capability is especially useful for tasks requiring data analysis, file processing, or other automated actions that require custom scripting. Select the Python option and load a Python interpreter as a data source to work with Python scripts during conversations with your agent.
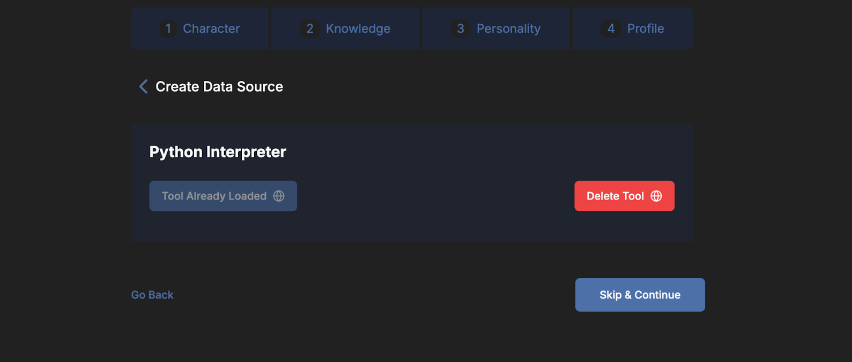
When Python is enabled, the agent can generate and execute scripts during a conversation. These scripts can access files uploaded in the chat or connected as data sources. You can also include instructions about which Python packages to use to guide script generation.The agent can install required Python packages within its execution environment.
📝 Note: Execution using Python is limited to 5 minutes per run.
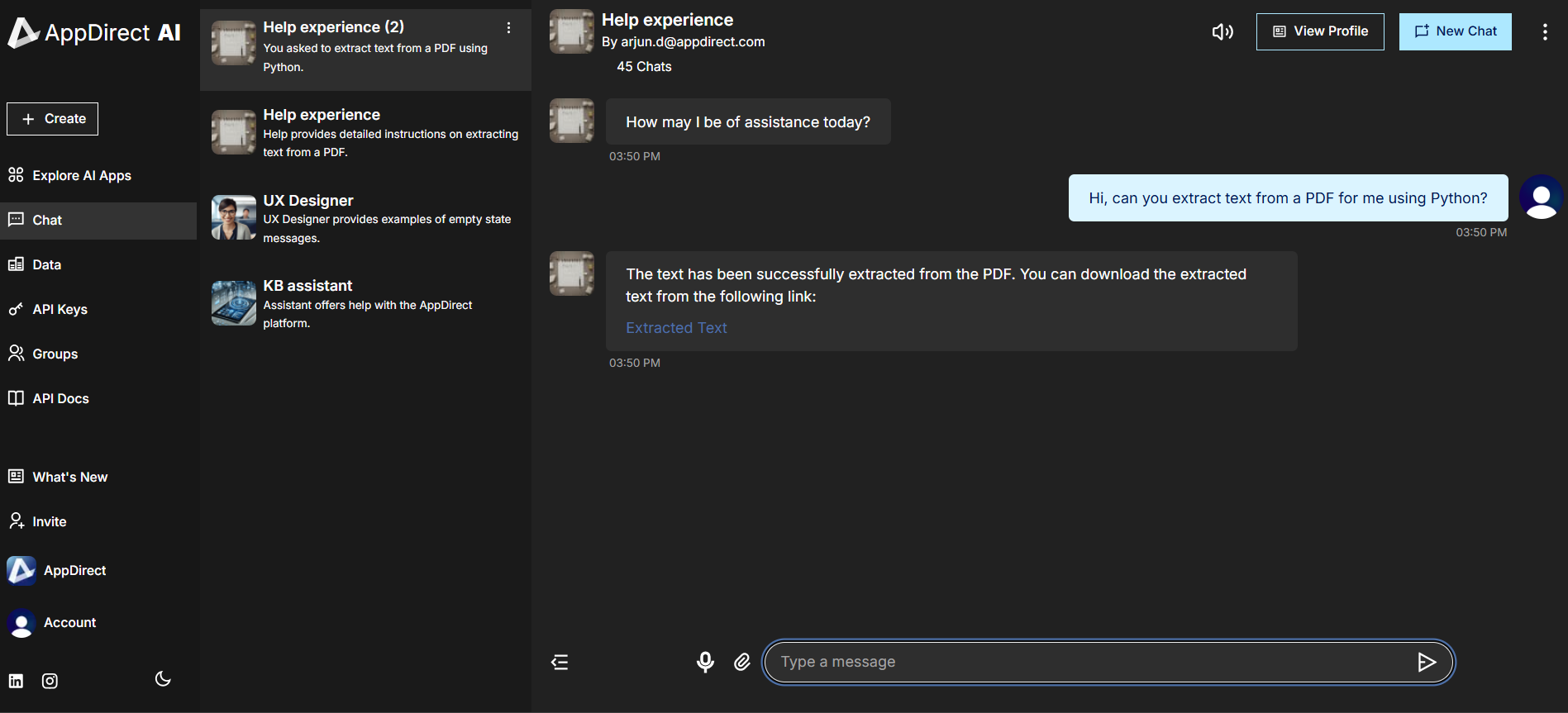
Without the Python tool enabled, an agent cannot run any scripts directly. It can only guide you on how to use scripts to perform any related tasks. See below to understand how the agent responds with and without the Python tool loaded when working with some PDF related tasks.
For example, to extract text from a PDF, the agent requires the Python tool to be enabled and the file to be available in its data sources. Without Python, the agent can describe the steps but cannot perform the extraction itself.

With the Python tool enabled, the agent proceeds to extract text using a script which runs in the background, provided you have uploaded the PDF to the agent knowledge base.
User Inputs
With this option enabled, an agent can ask users for specific information during a conversation. The agent renders structured input fields, such as text fields or selections, so users can provide the required data in a clear and consistent way. This is useful when an agent needs precise input to continue a task. Structured inputs help reduce ambiguity and improve the accuracy of responses.
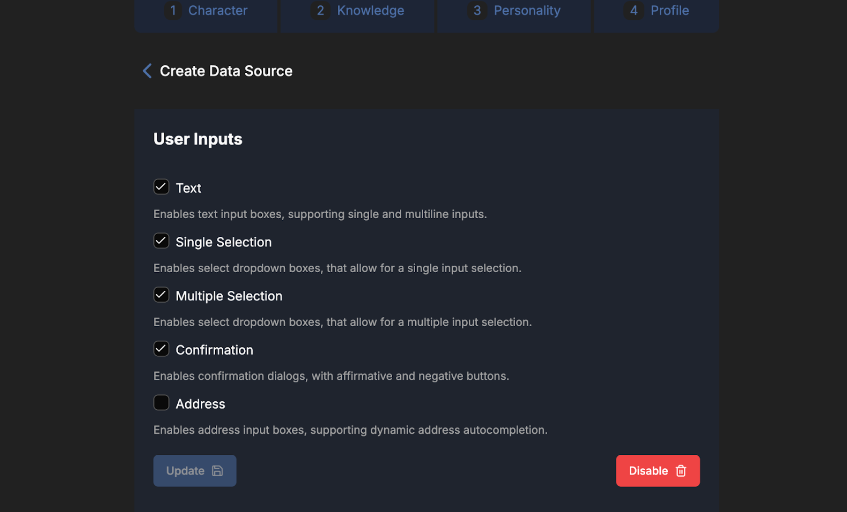
A common use case for utilizing input fields in a conversation with an agent is collecting an address. For instance, if you are building an agent to provide data based on a specific location, you can configure the agent to include an address input field. This field ensures users enter a valid address by leveraging the autocomplete functionality powered by Google Maps APIs. The agent would render a text field that dynamically suggests accurate addresses when you start typing.
📝 Note: For the best results, provide clear and well-defined instructions when using this feature.
Knowledge Retrieval
📝 Note: This feature is still in Beta.
The Knowledge Retrieval feature enables agents to access relevant information from a vector store built from uploaded data sources. With this feature, the agent can efficiently retrieve and utilize stored knowledge, providing answers based on a comprehensive, customized database.
Also known as Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), this process follows a sequential operation flow, where each step's output feeds into the next.
How It Works
-
Expand Queries (optional):
If enabled in advanced options, this step broadens the search by generating multiple related queries based on the original query. This expands the scope of retrieval to include a wider variety of relevant documents. -
Retrieve:
Retrieves documents that match the query from the vector store. You can set a limit for the number of documents to retrieve. -
Deduplicate:
Removes duplicate results when files appear across multiple data sources. -
Rerank:
Ranks documents based on relevancy using a dedicated machine learning model, which improves on the initial vector store ranking. Adjusting the retrieval document limit can improve accuracy and reduce noise. -
Enrich:
Adds metadata from the database to the retrieved documents. -
Grade:
Assesses document relevancy using a large language model (LLM). Relevant segments are highlighted, and documents receive a relevancy score from 0 to 10, with 10 being the highest. You can select a model for grading, though lighter models, such as GPT-4o Mini, are recommended to optimize data usage. Larger models may be reserved for specialized or complex topics. -
Filter:
Excludes results below the minimum relevancy score. -
Compress:
Removes irrelevant segments within documents to focus on pertinent information. -
Format:
Structures data in a format suitable for LLM processing.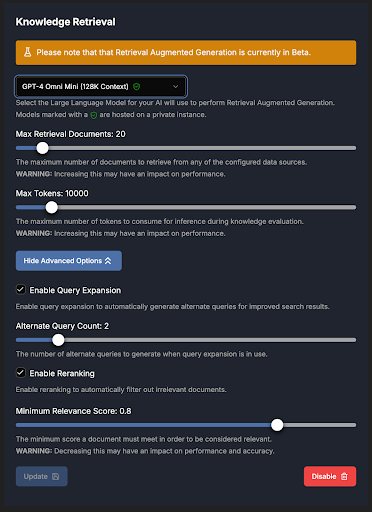
Web Search
The Web Search tool enables your agent to access real-time information from the web. Enable web search and select a language model so that the agent can retrieve up-to-date facts, news, or general knowledge that may not be available in the pre-trained model. This is useful for tasks that depend on recent events, changing information, or general factual lookups.
Image Generation
The Image Generation tool enables your agent to create images from prompts. This is useful for design, marketing, and creative use cases where visual output is needed.
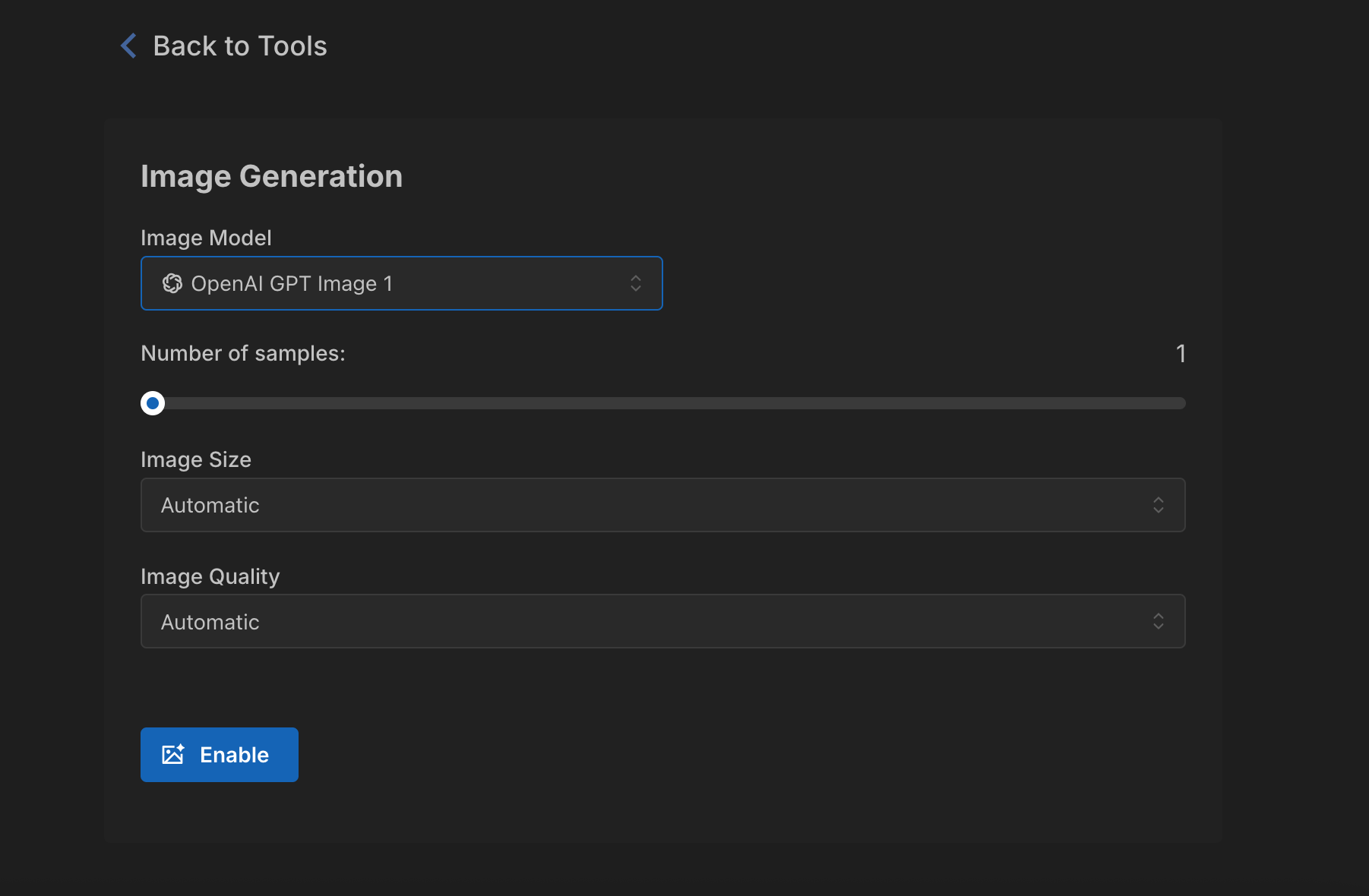
When you are configuring the tool, you can choose:
- Image Model - the model used for image generation.
- Number of samples - determines how many image variations are generated per prompt.
- Image Size - the dimensions for the image output.
- Image Quality - the quality of the image.
After configuring these options, enable the tool to allow the agent to generate images during conversations.
MCP Server
MCP servers allow agents to securely interact with external systems and tools. By connecting an MCP server, you can give your agents controlled read or write access to applications such as CRMs, email, calendars, code repositories, or other such application services.
MCP servers are perfect for action-oriented and automation-heavy use cases, where agents need to:
- Trigger actions in other applications
- Automate multi-step business processes
- Work with live or transactional data
For simpler question answering, data sources are sufficient.
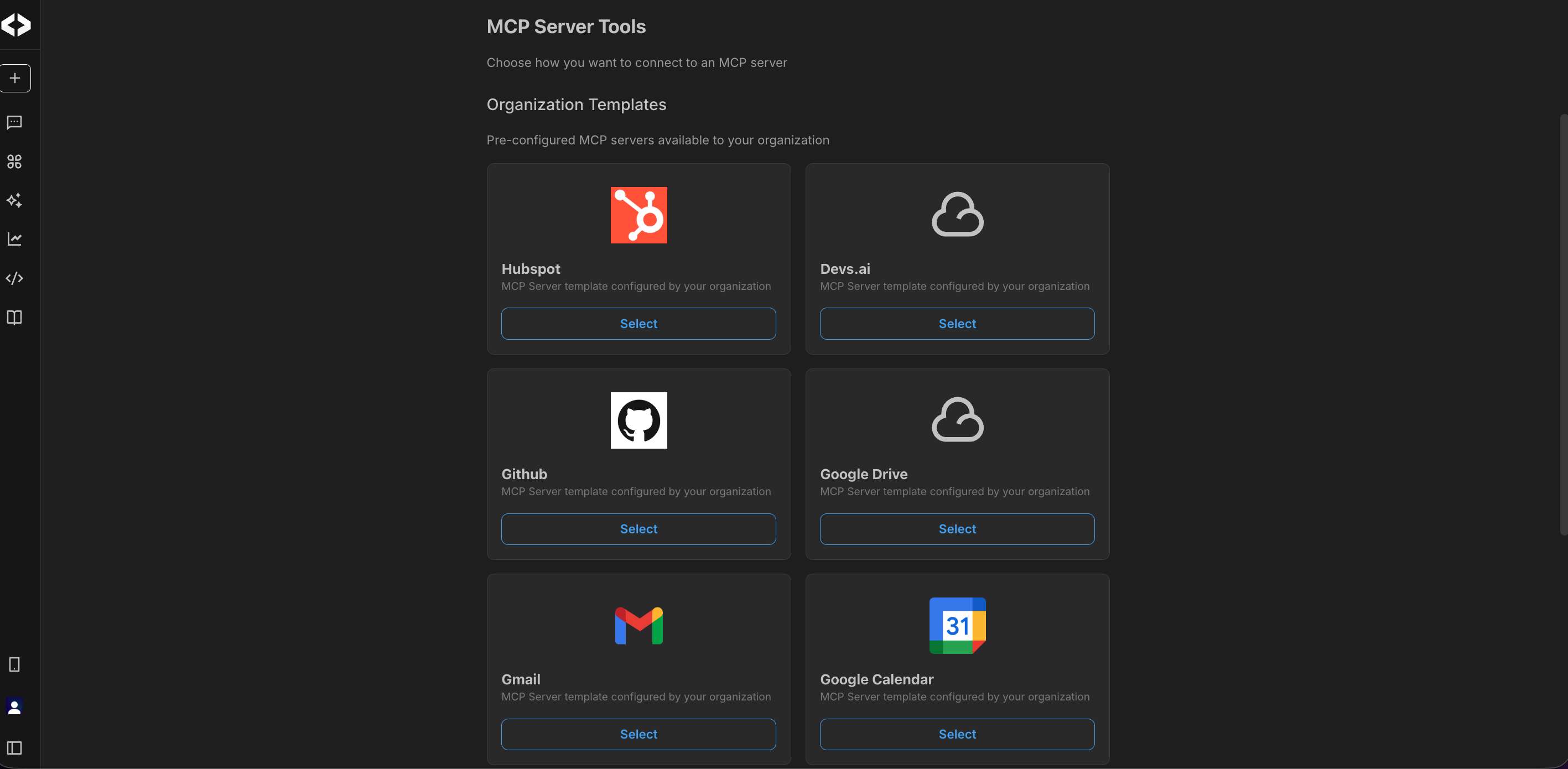
Using MCP server templates
The platform provides pre-configured MCP server templates for very commonly used applications. These templates simplify setup by predefining available tools, actions, and authentication requirements. Some of the pre-defined templates currently available are:
- HubSpot
- Gmail
- Google Calendar
- Code and storage tools such as GitHub and Google Drive
To use a pre-defined MCP server template,
- Open the MCP Server tool.
- Select a template from the available list.
- Review and select the tools that you want included.
- Complete any authentication if required.
- Save the configuration.
Once this is enabled, your agent can use the toolss that are included in the MCP server.
Using a custom MCP server
You can also connect a custom MCP server if you want to integrate with internal systems or other third-party services.
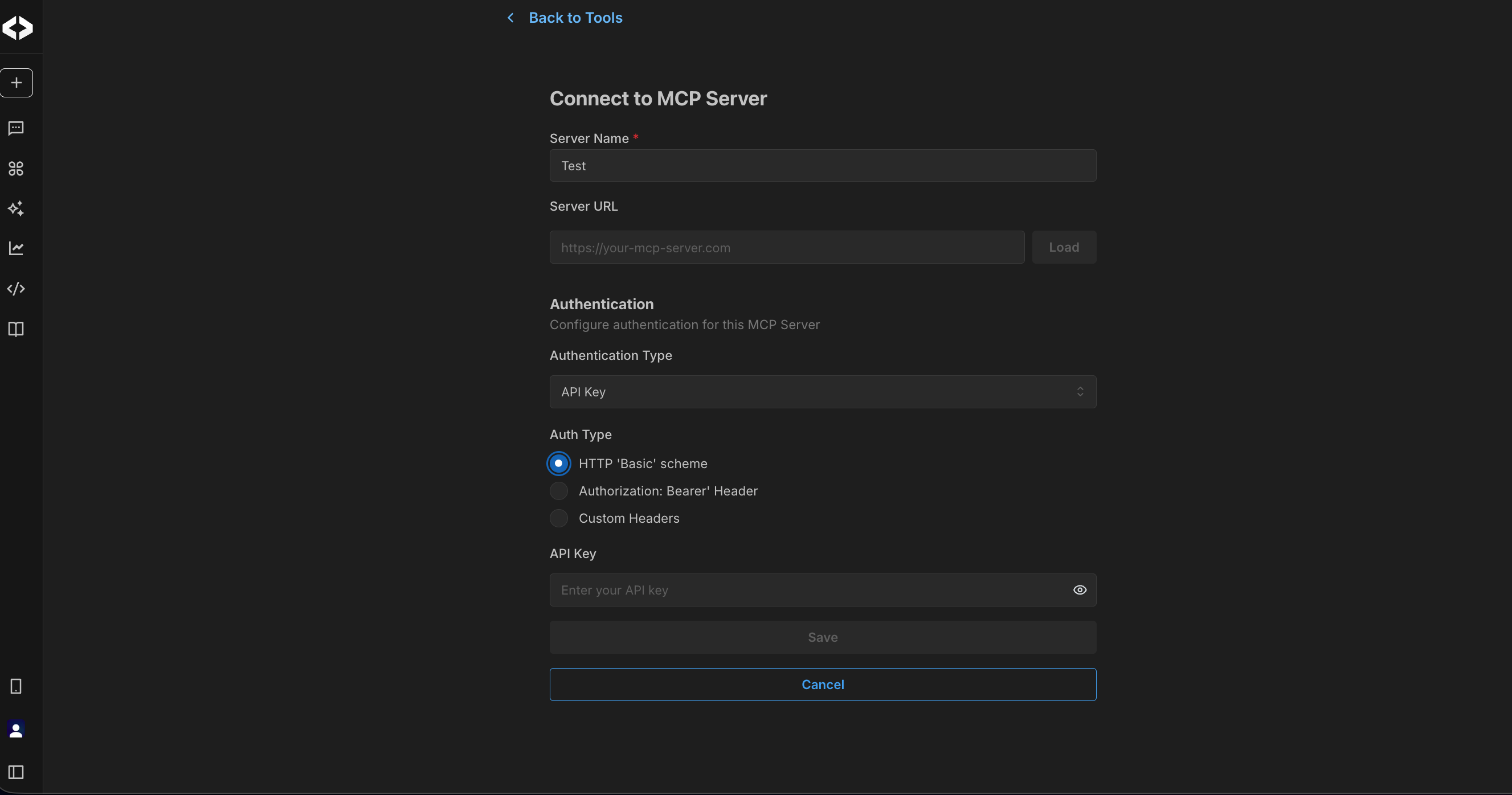
To create a custom MCP server,
- Select Create MCP Server.
- Enter a Server Name to identify the connection.
- Provide the Server URL for your MCP server endpoint.
- Choose an authentication type, such as:
- API key
- Authorization header
- Custom headers
- Enter the required authentication details.
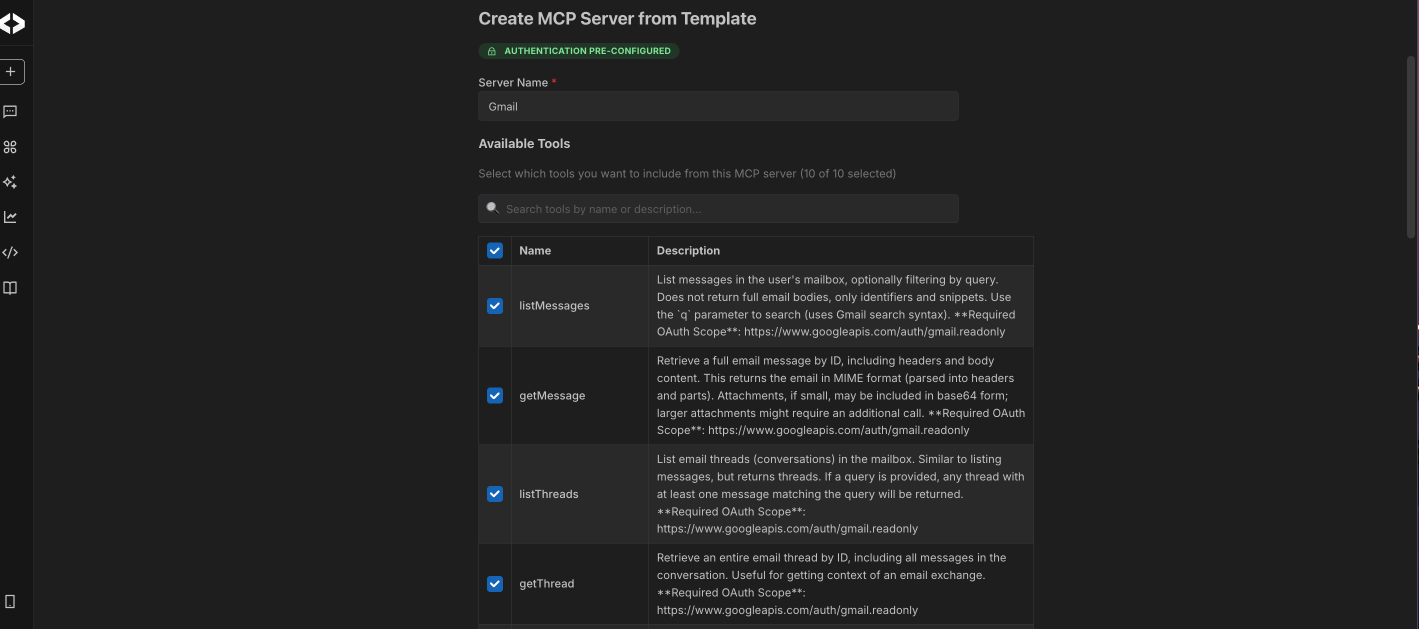
Managing MCP server tools
For both templates and custom servers, you can control which tools the agent can access. Each tool represents a specific capability, such as reading messages, creating records, or updating data. For example, if you connect a Gmail MCP server, the agent can use specific Gmail tools such as reading messages, listing threads, or retrieving email details. You can configure the server to allow read access. In this case, the agent can help with tasks like finding recent emails from a specific sender or match a particular subject.
Spreadsheet analysis
The Spreadsheet tool allows an agent to analyze and work with spreadsheet data in a structured manner. When enabled, an agent can read spreadsheet files and answer questions based on their contents, such as summaries, comparisons, and trends.
This is useful for use cases that involve numbers, tables, and repeated calculations:
- Financial analysis and reporting
- Working with pricing, usage, or billing data
- Summarizing large tables
- Comparing data across time periods
- Retrieving answers for calculations such as totals and averages
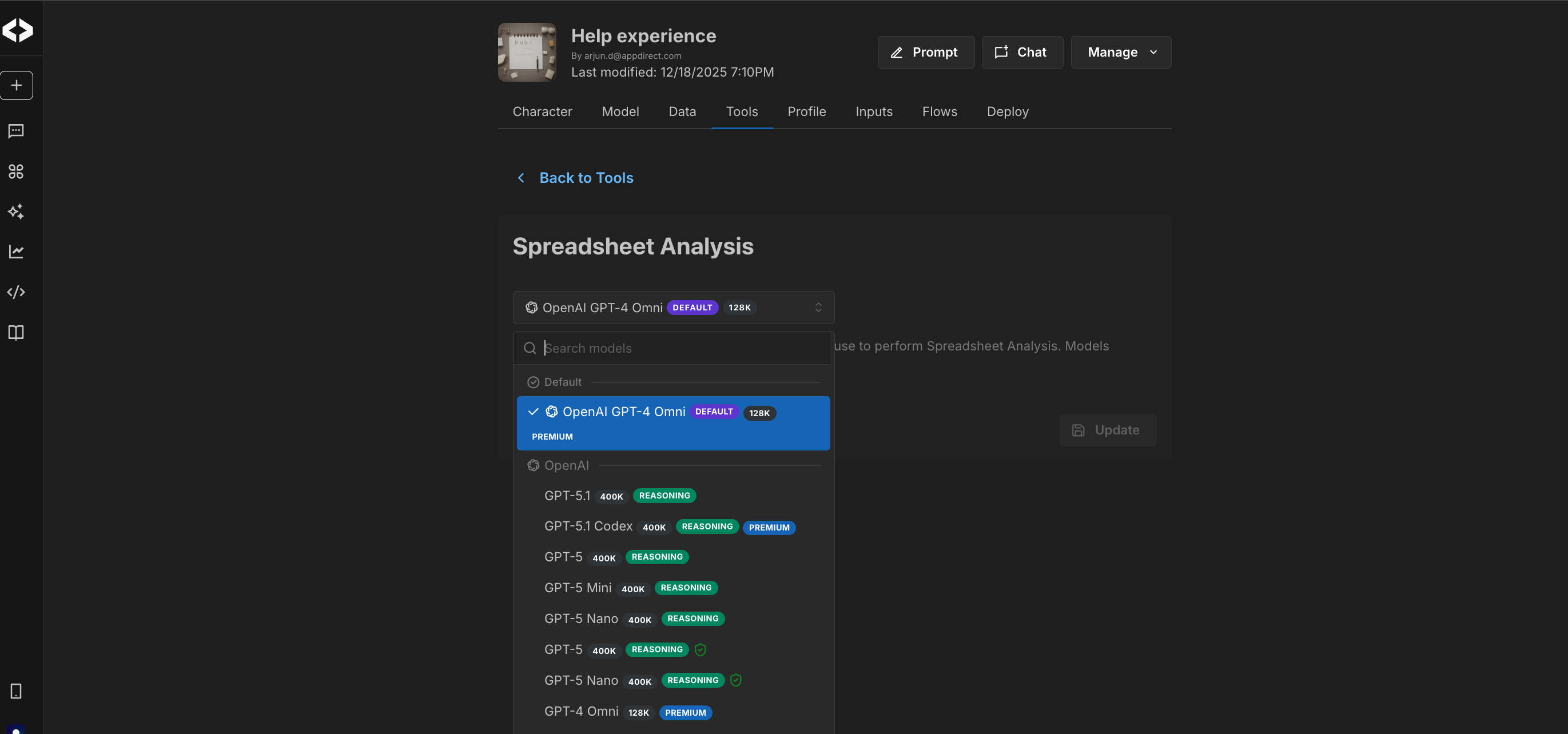
You can choose which language model the agent should use for spreadsheet analysis. Models with stronger reasoning capabilities are better suited for complex queries, while lighter models may be sufficient for simpler summaries.
If your spreadsheet contains large datasets or requires multi-step reasoning, it is recommended to test the agent with different models to find the best fit.
Browser
The Browser tool allows an agent to use a secure, controlled web browser to perform tasks on websites. When enabled, the agent can navigate web pages, interact with various page elements, and complete browser-based actions on your behalf. This is useful when a task cannot be completed easily through APIs or other data sources.
When you use the browser tool, agents can fill out forms on web pages, capture screenshots, or extract information. This allows the agent to handle tasks that normally require manual browsing.
Browser-based actions may take longer than API-based tasks and are also dependent on website layout. Changes in the layout can affect reliability. Use this tool only when other options are not availale. It is also recommended to test browser-enabeld agents before wider use.
Once tools are enabled, you can further shape how agents interact by configuring input fields and building workflows for more complex and structured behavior. To learn more, see Flows.